Open Source Components
Public Beta
Following the preliminary implementation roadmap (dependent on the legal process), the swiyu Trust Infrastructure is planned to go live with a full production roll out in 2026. To allowing future participants from the public and private sector to prepare themselves for the final go live, a Public Beta environment has been published.
The Public Beta environment aims to function as a basis for integration and experimentation efforts conducted by the ecosystem participants from both the public sector and the private sector. It provides the same technology that will be used by the productive environment in 2026. It’s operation and support are run on a best effort basis and is planned to be available beyond the full production roll-out in 2026 as an integration environment.
This participatory process is also helpful for testing and refining the infrastructure components, technological choices, and operation procedures under real world conditions.
Open Source Repositories
The source code of the swiyu Trust Infrastructure is publicly available under the MIT-License. This allows the Open Source community to integrate our components under permissive conditions. We welcome contributions and feedback in various forms. The options are described in the respective repositories and depend on the current development process:
-
Community Development: Core libraries and shared components are developed openly with the community, with ongoing updates.
-
Internal Development: Specific apps, registries, and components are developed privately and released publicly after each sprint. The published code can therefore only be a snapshot of the current development and not a thoroughly tested version.
The following components are available for Public Beta:
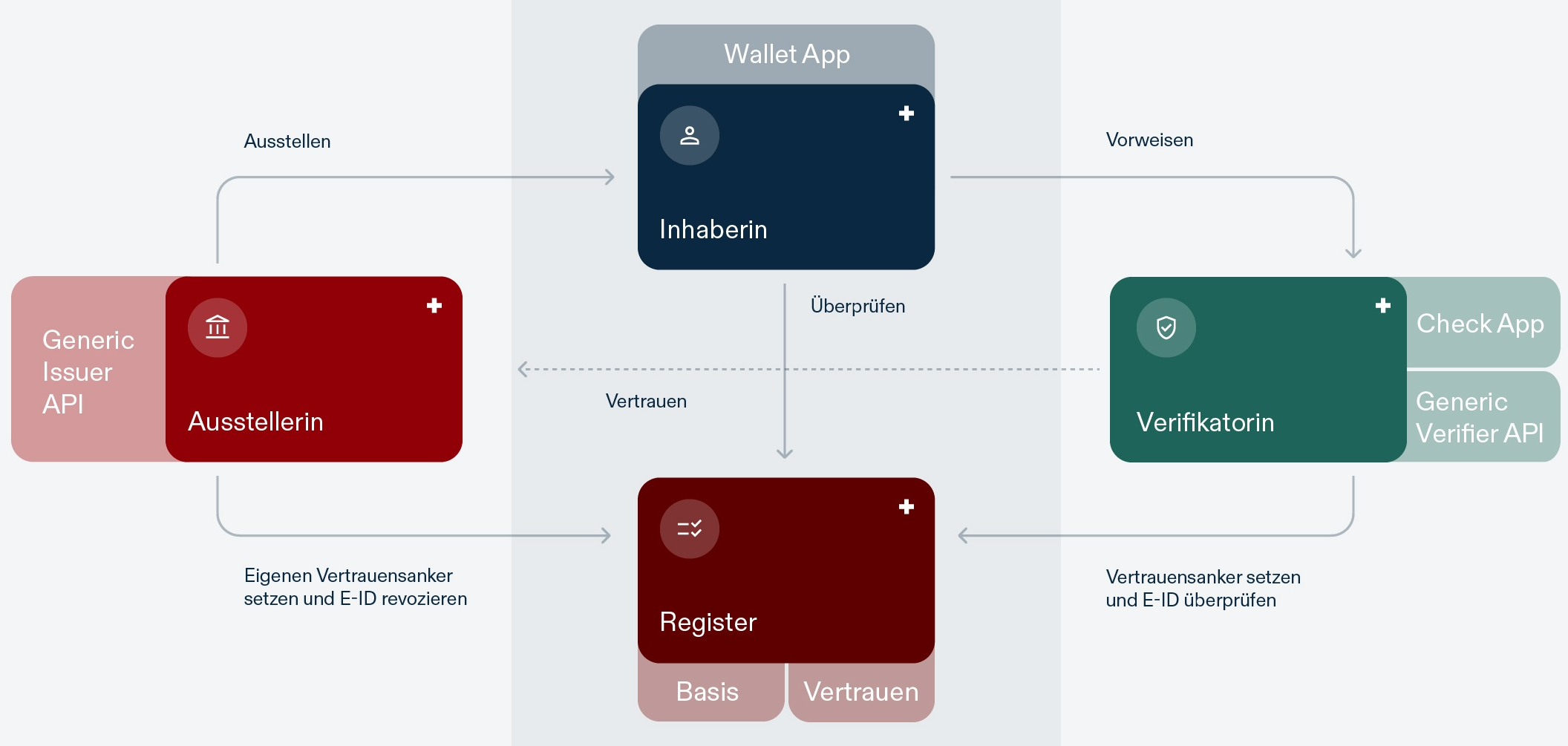
swiyu Base Registry
Entities can onboard, update, or offboard as issuers and verifiers within the ecosystem. The base registry will manage the public keys as part of the DIDDOC required for ecosystem interactions. Status lists containing information related to credential validity can be managed.
The source code is divided in different services:
- Base Registry Authoring Service
- Base Registry Data Service
- Status Registry Authoring Service
- Status Registry Data Service
swiyu Trust Registry
Entities can prove and maintain their status as verified issuers or verifiers, ensuring additional trust within the ecosystem. Users will be able to see the verification status of issuers and verifiers in their wallets and verifiers are able to validate the trust-status of the issuers.
The source code is divided in an authoring and a data service:
swiyu Generic Issuer
Entities can issue, revoke, suspend, and reactivate Verifiable Credentials (VCs), using the generic reference issuer implementation provided by the federal government.
The source code is available in the following repository:
swiyu Generic Verifier
Entities can integrate the reference verifier implementation to verify VCs, ensuring cryptographic integrity and validity according to their specific needs.
The source code is available in the following repository:
swiyu Android & iOS App
Users will be able to download the swiyu Public Beta Wallet, request Beta-ID credentials for testing purpose, manage their VCs and interact with the ecosystem.
The source code is available for iOS and Android:
DID Toolbox and DID Resolver
We developed different helpers to create and resolve DIDs. Creating DIDs involves a set of steps that are error prone or need some time to get familiar with and one might end up with invalid DIDs. The DID Toolbox supports you with various options for a quick start or advanced usage.
How to use the swiyu Public Beta Trust Infrastructure
The onboarding process for the swiyu Base- and Trust Registry and other use cases are documented in the Cookbook section. Advanced users will find more technical details in the different repositories. We integrate various technologies in the Swiss Trust Infrastructure. You can view the supported specifications and the integrated versions in the “Interoperability Profile”.